De-Ionized (DI) Water
Southwest Thermal's shell and tube heat exchangers are constructed from high quality materials with a sanitary finish, the ideal solution when cleaning is an essential part of the process. Our designs offer 100% drainable vessels with double tube sheets to guard against product cross contamination when required. The process side connections are sanitary. We offer optional electro polishing to increase sanitary performance and minimize corrosion. 3A certification is available.
- Multiple Designs: We offer DI Water heat exchangers in shell & tube, tube-in-tube, brazed plate, and plate and frame.
- Available Materials: Stainless steel, duplex stainless steel, as well as more corrosion-resistant alloys available.
- High Quality: All models constructed to the highest standards to extend life and provide maximum heat transfer.
- Efficiency: Offers top-of-the-line heat transfer efficiency for process fluids.
- Shell and Tube Classic shell and tube units are available in sizes ranging from 2" to 48". Larger custom units also available.
- Gasket Materials Numerous gasket materials available, including Viton, Silicone, Butyl, and Nitrile (NBR).
Shell & Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Evaporators & Condensors
- Clean-in-Place
- Stock and Custom Models Available
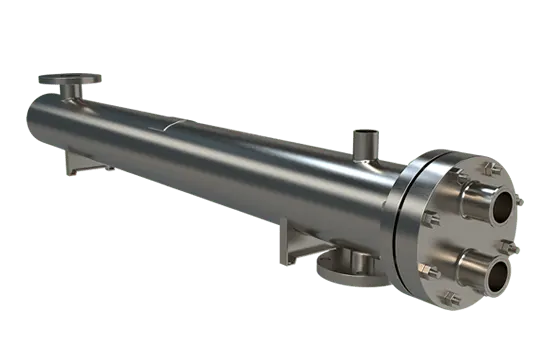
Plate & Frame:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- Multiple Materials Available
- Easy Service and Maintenance

Brazed Plate:
Sanitary Applications
- Compact Form Factor
- Multiple Materials Available
- Varous Connections

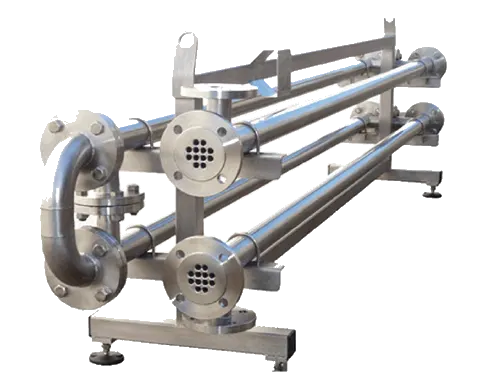
Tube-in-Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- High Temperature & Pressure
- Temperature Crossing
DI Water Heat Exchangers
Applications
The following is a list of typical processes that require heat exchangers of this type. API or formulated pharmaceuticals, blood, plasma or growth media, WFI, USP, DI, RO and CIP heating /cooling, pure steam generation & condensing, bio kill & waste neutralization, and point of use cooling and/or heating.
Sizes & Materials
Our shell and tube heat exchangers are constructed from high quality materials with a sanitary finish, the ideal solution when cleaning is an essential part of the process. Our designs offer 100% drainable vessels with double tube sheets to guard against product cross contamination. The process sided connections are sanitary. We offer optional electro polishing to increase sanitary performance and minimize corrosion.
We carry DI water shell and tube heat exchangers from 2" to 48" shell diameters up to 65 feet in length. Multiple design styles such as multi-pass, U-tube, straight tube, and double tube sheet units are available. Our construction materials include 304L, 316L, and duplex stainless steels such as 2205, 2507, and Zeron 100. Additionally, corrosion resistant alloys like Hastelloy, Alloy 20, Monel 600, AL-6XN, Titanium and copper-nickel alloys are also available.
Tube-In-Tube
Tube-in-tube heat exchangers can be utilized when fluids contain significant amount of fibers or other suspended particles. This type of exchanger is formed by two concentric tubes which are corrugated to enhance the heat transfer rate and reduce the overall size of the exchanger. Product wetted components are manufactured from 316L stainless steel. Duplex stainless steel materials are available for more aggressive fluids. All areas not in contact with the product are constructed from 304 stainless steel.
Plate Heat Exchangers
We also offer brazed plate heat exchangers available in stainless steel and various alloys to meet the stringent demands of DI water applications. These compact exchangers offer maintenance free operation and allow for very close approach temperatures between fluids at economical pricing.


