Heat Exchanger for Biopharma
Sanitary Heat Exchangers for BioTech
In the biotech industry, specialized heat exchangers are critical for processes such as fermentation, cell culture, and enzyme reactions. These systems ensure that sensitive materials are treated under optimal conditions, preserving their desired qualities while enabling efficient heat transfer.
Exchangers for Strict Hygiene Standards
Sanitary heat exchangers play a crucial role in maintaining stringent hygiene standards to prevent contamination. Designed to meet rigorous sanitary regulations, these exchangers are tailored for easy cleaning and sterilization, which prevents cross-contamination and ensures product safety. This is particularly important in processes involving proteins, vaccines, and other pharmaceutical agents where even minimal contamination can compromise product efficacy and safety.
Configurations
The configurations of these heat exchangers are diverse, including shell and tube and plate and frame types, selected based on the specific needs of a biological process. For example:
Plate Heat Exchangers: Ideal for systems requiring rapid heating or cooling, such as in the pasteurization of pharmaceutical products, due to their high surface area to volume ratio.
Shell and Tube Exchangers: Preferred for processes involving high temperature or pressure parameters, offering robustness and reliability. Emphasis on Energy Conservation
Engineered with a focus on energy conservation, sanitary heat exchangers are designed to reclaim waste heat and repurpose it within the facility. This contributes to reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs.

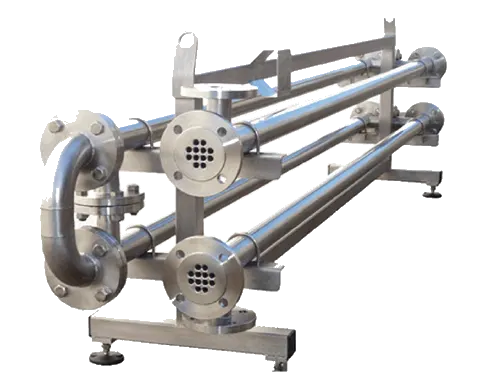
Shell & Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Evaporators & Condensors
- Clean-in-Place
- Stock and Custom Models Available
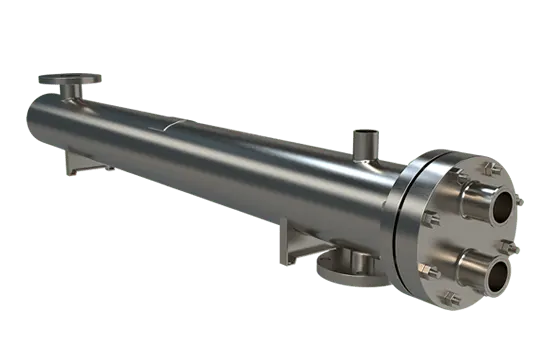
Plate & Frame:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- Multiple Materials Available
- Easy Service and Maintenance

Brazed Plate:
Sanitary Applications
- Compact Form Factor
- Multiple Materials Available
- Varous Connections

Tube-in-Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- High Temperature & Pressure
- Temperature Crossing