Shell & Tube
These devices facilitate heat transfer between two fluids while adhering to stringent hygiene standards required in industries such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, cosmetics, and more. In these sectors, the product's integrity is paramount, and any risk of cross-contamination can lead to product recalls, financial loss, and harm to public health. These devices facilitate heat transfer between two fluids while adhering to stringent hygiene standards required in industries such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, cosmetics, and more. In these sectors, the product's integrity is paramount, and any risk of cross-contamination can lead to product recalls, financial loss, and harm to public health.
The structure of a sanitary shell and tube heat exchanger typically involves a series of tubes enclosed within a shell. One fluid flows through the tubes while the other fluid circulates around the tubes within the shell, allowing for the efficient transfer of energy in the form of heat. The construction of these exchangers prioritizes smooth surfaces with minimal crevices to minimize bacterial growth and facilitate ease of cleaning. They are commonly equipped with features that enable complete drainage, and the use of high-purity materials that withstand both the aggressive cleaning protocols and the demands of high-temperature processes.
Applications of these heat exchangers vary widely, including pasteurization, sterilization, temperature regulation of fermentation processes, and cooling of products prior to packaging. Their role is critical in maintaining the desired temperature and assuring consistent quality in the production flow. Rather than a one-size-fits-all solution, these heat exchangers are often customized for specific applications, taking into account factors such as flow rate, viscosity of the fluids, and temperature profiles to meet the exacting needs of each industrial process.
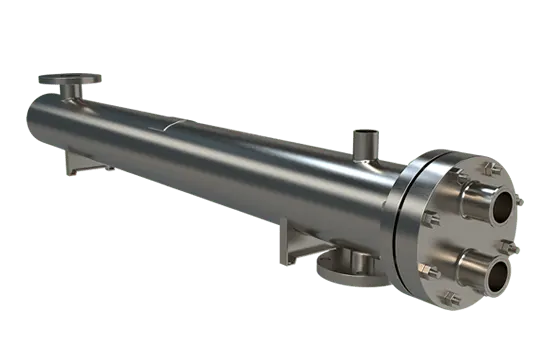
Configuration
Lenght:
12" to 400"
Diameter:
3" to 48"
Code:
ASME / TEMA
Standard Features
- Product Contact Surfaces Polished to 32 RA Finish
- Exterior Polished to a 40 RA Finish
- Fully Drainable and Easily Cleanable in CIP Mode
- Channel Head is Milled out of a Single Solid Piece of Stainless Steel
- ASME Approved Sanitary Ferrules
- Assembly Polished to Meet Exacting Sanitary Requirements
- Seal-Welded Tubes to Tubesheet with Orbital TIG Welding
- ASME Code "U" Stamp and National Board Registration
- Hydro Static Pressure Testing
- Dye Penetrant Testing
- Passivation
Sanitary Shell and Tube Stainless Steel Heat Exchangers
In industries with stringent sanitary standards, such as pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, and dairy, specialized sanitary heat exchangers are necessary to ensure compliance.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Sanitary shell and tube heat exchangers are essential in maintaining high cleanliness standards in the food, beverage, dairy, and personal care industries. Many clients rely on these exchangers for their durability and regulatory compliance.
Sanitary Heat Exchangers
Sanitary shell and tube heat exchangers are available both in stock and custom designs. They offer features like 100% 304L or 316L stainless steel construction for corrosion resistance and sanitary considerations. Built to TEMA Class C and ASME hydro-tested with a code stamp, these exchangers handle low-fouling fluids for heating or cooling. Sanitary tri-clamp connections are commonly used, and U-tube design allows tubes to expand or contract. Similarly, shell expansion bellows are available for high temperature swing applications. O-rings and tube bundles are replaceable, with sizes ranging from 4" x 36" to 10" x 54", and upgrades are available to meet the current 3-A Sanitary Standard.
Standard designs feature 304L stainless steel tubing, welded and bright annealed, with a 40Ra exterior finish. Custom upgrades include 316L stainless steel, 3-A compliant seamless tubes polished to 32Ra surface roughness, welded tube-to-tube sheet joints, chloride and asbestos-free insulation jackets, and options for vertical mounting supports or horizontal saddles. Additional options include sight glasses, vacuum breakers, level gauge ports, ASME flanged connections, NPT threaded or sanitary tri-clamp connections, double tube sheets, expansion joints, floating tube sheets, passivation and electropolished surfaces, davit arms, CIP spray ball assemblies, and condensate collection chambers.

Design Requirements for Sanitary Heat Exchangers
Design specifications vary by industry and application, but common requirements include seal welding of tube-to-tube sheet joints, sanitary tri-clamp fittings, polished surfaces, compliance with the 3-A Sanitary Standard, and use of PTFE, Viton©, Gylon, or other gasket materials. Clean-in-place design and ASME BPE compliance with sanitary fittings are also crucial.
Applications of Sanitary Heat Exchangers
Sanitary heat exchangers are pivotal in food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and dairy industries, significantly reducing microbial activity to keep products safe, prevent spoilage, and meet regulatory standards. They are versatile, applicable in processing, filling, drying, and concentration stages, and can handle products of varying viscosities.
Industries that commonly use sanitary shell and tube heat exchangers include refrigeration, power plants, HVAC systems, food processing, chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and waste heat recovery. They are also employed in cheese and milk pasteurization, beer and wort cooling, beverage pasteurization, ultra-high temperature sterilization, juice pasteurization, bottled water treatment, liquid egg processing, and heating or cooling of condiments, starches, soups, and sauces, as well as steam generation.
Benefits of Sanitary Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube exchangers are customizable, proven, and versatile. They are suitable for various applications due to their adaptable sizes and configurations. Environmentally friendly, they operate continuously to prevent overheating without relying on additional equipment, thus using less energy. Lower operating costs further enhance their appeal, as they require minimal maintenance and operation expenses.
Additional benefits include the ability to process fiber or particulate products, high working pressure and temperature capacity, simple inspection and disassembly, high security in aseptic processes, and easy customization.
TEMA Standards
Our shell and tube heat exchangers adhere to the standards set by the Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association (TEMA), ensuring consistency and long-term reliability. Products meet TEMA classes B, C, and R, depending on the application and customization.
3A Sanitary Standard
Certified to build heat exchangers meeting the 3-A Sanitary Standard, we work with food and dairy clients, ensuring designs and fabrication practices meet these standards. Clients can expect the heat exchangers to pass sanitary inspections without deficiencies.
Clean-in-Place
A leading supplier of Clean-in-Place sanitary shell and tube heat exchangers in the US, we offer stock products in various sizes for compatibility. Thermal modeling software ensures applications work with stocked products. For custom solutions, a dedicated team of engineers and designers adopts a consultative approach to meet your specific needs.
Additional Upgrades
Upgrades for existing sanitary shell and tube heat exchangers include stainless steel jacket cladding and insulation, mounting saddle supports, connection and baffle modifications for liquid applications, upgrades to meet the 3-A Sanitary Standard, passivation or electro-polished contact surfaces, material upgrades (Duplex, Hastelloy, 316L SS, AL6XN, and other alloys), multiple pass designs, and bonnets for better tube side velocity in tight spaces.
Common FAQs
Sanitary Applications

SANITARY EXCHANGERS
(CIP) Clean in Place
CIP heat exchangers are designed for efficient cleaning-in-place processes in sanitary applications, enhancing productivity and hygiene.
+ Learn More
FOOD & BEVERAGE • ALCOHOL
Alcohol Production
Heat exchangers are widely used in the production of beer, wine, and distilled spirits.
+ Learn More
FOOD & BEVERAGE • DAIRY
Dairy Exchangers
From pasteurization to heating and cooler viscous fluids like yogurt, sanitary exchangers play a key role.
+ Learn More

