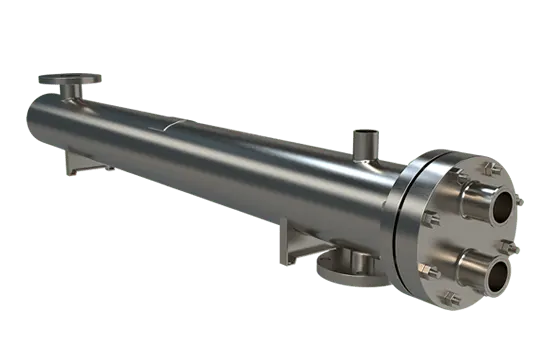
Beverage Grade Heat Exchangers
Heat recovery is another important application for these systems, enabling manufacturers to harness excess thermal energy from hot fluids and repurpose it to preheat cold fluids entering the system. This not only maximizes energy efficiency but also reduces operational costs. With sustainability and energy conservation becoming increasingly vital within the industry, the implementation of heat exchangers serves as a testament to technological advancements and a commitment to environmentally conscious practices.
Whether dealing with sanitation compliance, efficiency, or process control, the utilization of heat exchangers within the beverage industry is indispensable. Manufacturers rely on these robust systems to ensure production runs smoothly, and that each beverage meets both safety standards and consumer expectations.
Common FAQs
Beverage heat exchangers regulate temperatures during production and storage in the beverage industry. Beverage heat exchangers facilitate the transfer of heat between two liquids, by cooling or heating liquid beverages without mixing them with the cooling or heating medium. Exact temperature control is essential for quality, flavor, and shelf life for beverages like beer, wine, juices, dairy drinks, and soft drinks. Beverage heat exchangers support pasteurization, where elevated temperatures are applied to destroy harmful microorganisms, and include rapid cooling to stabilize the beverage before bottling.
Types of heat exchangers used by beverage manufacturers include:
- Plate Heat Exchangers: Used in the dairy and juice industries for pasteurization, and cooling, plate heat exchangers use thin, flat plates stacked together to transfer heat using minimal energy.
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers: Using a cylindrical shell with multiple tubes is ideal for handling high-pressure or high-volume applications in breweries.
- Tubular Heat Exchangers: Tubular heat exchangers handle thicker beverages without clogging, and are ideal for viscous or pulp-laden liquids.
Beverage heat exchangers maintain product safety, prevent spoilage, and preserve taste, making them important for beverage processing.
Beverage heat exchangers regulate temperature by transferring heat between a beverage and a separate heating or cooling fluid, ensuring the fluids donít mix together. The beverage flows through channels or tubes that are surrounded by the heating or cooling fluid, allowing heat to be absorbed or released. Thin metal plates in plate heat exchangers create parallel channels, allowing the beverage and cooling or heating fluid to flow in opposite directions. This counterflow increases heat transfer, making it work well for pasteurization processes or rapid cooling.
In shell and tube or tubular heat exchangers, the beverage flows through tubes within a larger shell holding the heating or cooling fluid. Heat transfers through tube walls so the fluids flow past each other in separate compartments, making the beverage's temperature rise or lowering it.
Beverage heat exchangers maintain temperature control using indirect heat transfer, which helps ensure beverage quality, safety, and consistency.
By facilitating heating and cooling procedures necessary for beverage production quality, cleanliness, and safety, beverage heat exchangers offer companies in the heatable beverage market some advantages. They maintain constant temperatures for pasteurization and clean-in-place (CIP)systems while heating cleaning solutions to eliminate residue from system components.
They supply warm water for cleaning production equipment such as tanks and piping. Compact, skid-mounted designs maximize industrial factory floor space while providing flexible positioning for CIP equipment. By generating turbulence at adequate flow rates, their designs provide heat transmission and self-cleaning without risking cross-contamination between liquids.
Regenerative heat transfer reuses heated fluids while conserving energy over cycles. Plate heat exchangers deliver up to five times more heat transfer than shell-and-tube models, creating cost savings and improved productivity.
In beverage production, temperature management is important for ensuring both safety and quality. By preventing excessive heat exposure, which can deteriorate flavor, color, and nutritional ingredients, precise temperature adjustments help preserve these qualities. Heat exchange stability preserves product consistency between batches and safeguards beverages during processes. Temperature balance management minimizes energy consumption and improves production by reducing the risk of reprocessing batches that fail to meet quality standards.
Beverage heat exchangers improve product shelf life by providing precise temperature control for essential processes like rapid cooling and pasteurization. Heat exchangers raise the beverage to an optimal temperature during pasteurization, eliminating harmful microorganisms and enzymes that may cause spoilage. This controlled heating, followed by cooling, stabilizes the product before bottling, preventing unwanted bacterial growth or fermentation that can affect shelf life. By ensuring consistent temperatures and preventing contamination, beverage heat exchangers preserve quality, taste, and nutritional value over time.