Heat Exchanger For Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical
The functionality of heat exchangers in pharmaceutical environments extends to several key operations including the heating, cooling, and pasteurization of products, as well as maintaining the necessary thermal conditions for various aspects of medication production.
The design of heat exchangers for pharmaceutical use adheres to stringent industry standards, ensuring contamination risks are minimized and processes remain compliant with health regulations. The equipment often features high-quality materials that withstand corrosive substances and rigorous cleaning protocols. Stainless steel is a commonly used material for its durability and resistance to a wide range of chemicals. Additionally, the internal surfaces can be polished to a finish that greatly reduces the possibility of product adhesion and bacterial growth, facilitating easier cleaning and sterilization. Units meeting 3-A sanitary standards can be produced upon request.
The technology employed in pharmaceutical heat exchangers includes innovations to enhance energy efficiency and performance. The incorporation of features such as double-tube sheets and leak detection mechanisms provides extra assurance against cross-contamination, a crucial factor in pharmaceutics where product purity is paramount. Heat recovery systems may also be integrated into the design, allowing for sustainable practice by repurposing excess heat generated during operations.
For processes that require precise temperature management, such as the liquefaction of viscous mixtures or the cooling of solutions to prevent degradation of active compounds, the heat exchangers must offer high levels of thermal transfer efficiency and the ability to operate consistently under varying load demands. The configuration can vary from shell and tube to plate and frame, each uniquely suited for different tasks within the pharmaceutical production cycle.

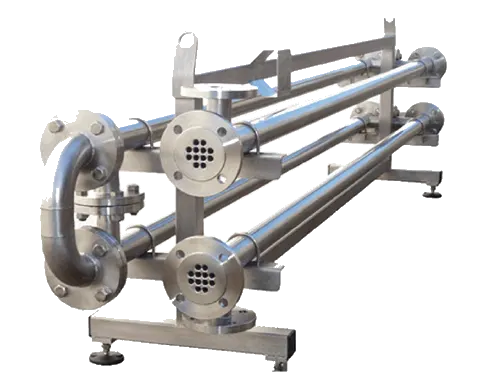
Shell & Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Evaporators & Condensors
- Clean-in-Place
- Stock and Custom Models Available
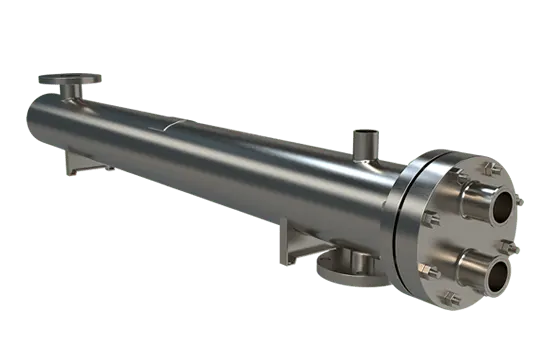
Plate & Frame:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- Multiple Materials Available
- Easy Service and Maintenance

Brazed Plate:
Sanitary Applications
- Compact Form Factor
- Multiple Materials Available
- Varous Connections

Tube-in-Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- High Temperature & Pressure
- Temperature Crossing