Water for Injection (WFI) Heat Exchangers: Ensuring Sterile and Safe Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry's heartbeat is its commitment to the production of safe and sterile medications, a task that hinges greatly on the quality of Water for Injection (WFI). A critical component in the preparation of WFI is the heat exchanger, a device that plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the sterilization process meets stringent regulatory standards.
What is WFI?
Water for Injection (WFI) is depyrogenated water of a high purity, devoid of any additives, and free from microbial contamination. It is used as a solvent or diluent for the preparation of drugs that are administered intravenously, as well as for cleaning processes where even trace amounts of impurities or contaminants are unacceptable.
The Vital Role of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers in the WFI production process are tasked with transferring heat efficiently and effectively, either for the heating step in the WFI generating process or for the cooling step before the WFI is used or stored. These specialized heat exchangers must be designed to meet strict pharmaceutical standards to avoid any risk of contamination.
Sterilization and Temperature Maintenance
A key requirement for a WFI heat exchanger is its ability to maintain high temperatures to ensure that water remains sterile. Sterilization may require temperatures above 80°C, which heat exchangers must consistently maintain to avoid any microbial growth. Such stringent controls protect the manufacturing process and, ultimately, the patients who receive the pharmaceutical products.
Material and Design Considerations
To prevent corrosion and bacterial growth, WFI heat exchangers are commonly constructed from high-grade stainless steel, which withstands high-temperature operation and ensures long-term durability. Additionally, the design often features a smooth, crevice-free surface to discourage any bacterial attachment and proliferation.
The configuration of WFI heat exchangers generally opts for a double-tube sheet design, which prevents any cross-contamination between the WFI and the heating or cooling mediums. This is crucial in avoiding the introduction of impurities into the WFI during heat exchange.
Energy Efficiency
Modern heat exchangers are also designed with the optimization of energy use in mind. These systems utilize advanced technology to recover and reuse heat within the production cycle, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint and operational costs. Such energy efficiency is not only environmentally responsible but also aligns with the growing global demand for more sustainable manufacturing processes.
Cleanability and Maintenance
Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Sterilize-in-Place (SIP) procedures are critical for WFI heat exchangers. Regular maintenance and cleaning protocols are essential to ensuring the continuous production of WFI that meets stringent purity standards. An effectively designed heat exchanger will support these protocols without compromising the sterility of the product.
Applications in the Pharmaceutical Industry
WFI heat exchangers are ubiquitous across the pharmaceutical sector, employed in areas such as:
- Preparation of Parenteral Solutions: From simple hydration fluids to complex nutrient cocktails for patients unable to consume food orally.
- Equipment Cleaning: Ensuring that machinery and tools engaged in drug manufacture are devoid of microbial life or unwanted chemical residues.
- Product Temperature Control: Critical in the manufacturing and storage of thermally sensitive pharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
The role of the heat exchanger in the context of WFI for the pharmaceutical industry cannot be overstated. Their contribution to maintaining sterility and safety standards is invaluable, underpinning every facet of drug preparation that involves water. With technological advancements, these systems are not only becoming more effective but are also contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective production environment. Ensuring that water used in pharmaceuticals is pure and sterile allows the industry to uphold its primary commitment—safeguarding patient health and wellbeing.
In a sector where there is no margin for error, WFI heat exchangers emerge as unsung heroes, allowing manufacturers to deliver high-quality, safe, and effective medical products, time and time again.
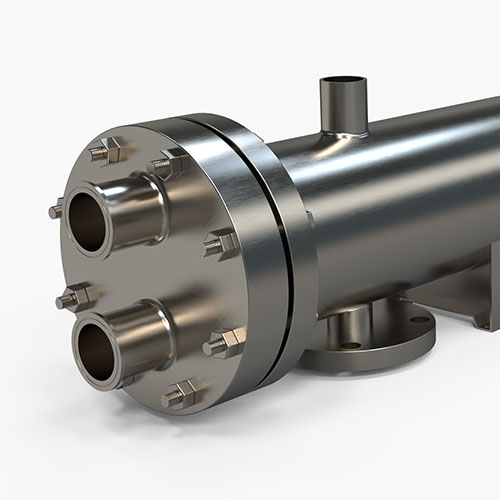

Shell & Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Evaporators & Condensors
- Clean-in-Place
- Stock and Custom Models Available
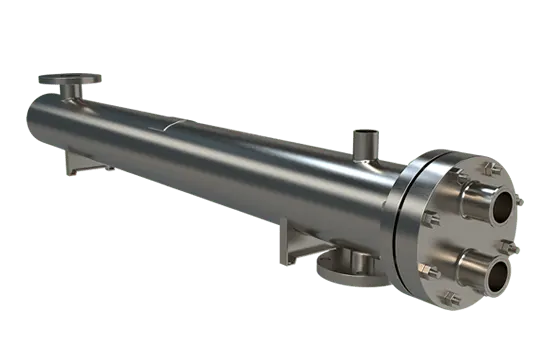
Plate & Frame:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- Multiple Materials Available
- Easy Service and Maintenance

Brazed Plate:
Sanitary Applications
- Compact Form Factor
- Multiple Materials Available
- Varous Connections

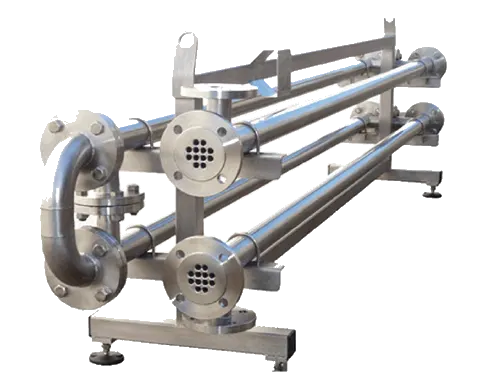
Tube-in-Tube:
Sanitary Applications
- Fully Customizable
- High Temperature & Pressure
- Temperature Crossing
More About Direct Injection
Direct Injection (DI) is a water purification process that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove molecules, ions, and larger particles from drinking water. Direct injection can remove many types of suspended and dissolved species from water, including bacteria, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water.
HeatX’s shell and tube heat exchangers are constructed from high quality materials with a sanitary finish, the ideal solution when cleaning is an essential part of the process. Our designs offer 100% drainable vessels with double tube sheets to guard against product cross contamination when required. The process sided connections are sanitary. We offer optional electro polishing to increase sanitary performance and minimize corrosion. 3A certification is available.
Shell and Tube
We offer DI water shell and tube heat exchangers from 2" to 48" shell diameters up to 65 feet in length. Multiple design styles such as multi-pass, U-tube, straight tube, and double tube sheet units are available. Our construction materials include 304L, 316L, and duplex stainless steels such as 2205, 2507, and Zeron 100. Additionally, corrosion resistant alloys like Hastelloy, Alloy 20, Monel 600, AL-6XN, Titanium and copper-nickel alloys are also available.
Tube-in-Tube
Tube-in-tube heat exchangers can be utilized when fluids contain significant amount of fibers or other suspended particles. This type of exchanger is formed by two concentric tubes which are corrugated to enhance the heat transfer rate and reduce the overall size of the exchanger. Product wetted components are manufactured from 316L stainless steel. Duplex stainless steel materials are available for more aggressive fluids. All areas not in contact with the product are constructed from 304 stainless steel.
Brazed Plate
We also offer brazed plate heat exchangers available in stainless steel and various alloys to meet the stringent demands of DI water applications. These compact exchangers offer maintenance free operation and allow for very close approach temperatures between fluids at economical pricing.
Gasketed Plate (Plate & Frame)
HeatX offers plate and frame exchangers to satisfy the high demands of demineralized water heat transfer. These are constructed of 304 or 316 stainless steel. Plate separation is handled by gaskets of various materials depending on your design requirements. Some of the choices in gasket materials include Nitrile (NBR), Silicone, EPDM, Viton, or Butyl.
The following is a list of typical processes that require heat exchangers of this type. API or formulated pharmaceuticals, blood, plasma or growth media, WFI, USP, DI, RO and CIP heating /cooling, pure steam generation & condensing, bio kill & waste neutralization, and point of use cooling and/or heating.
HeatX’s shell and tube heat exchangers are constructed from high quality materials with a sanitary finish, the ideal solution when cleaning is an essential part of the process. Our designs offer 100% drainable vessels with double tube sheets to guard against product cross contamination. The process sided connections are sanitary. We offer optional electro polishing to increase sanitary performance and minimize corrosion.
HeatX has DI water shell and tube heat exchangers from 2" to 48" shell diameters up to 65 feet in length. Multiple design styles such as multi-pass, U-tube, straight tube, and double tube sheet units are available. Our construction materials include 304L, 316L, and duplex stainless steels such as 2205, 2507, and Zeron 100. Additionally, corrosion resistant alloys like Hastelloy, Alloy 20, Monel 600, AL-6XN, Titanium and copper-nickel alloys are also available.
We also offer brazed plate heat exchangers available in stainless steel and various alloys to meet the stringent demands of DI water applications. These compact exchangers offer maintenance free operation and allow for very close approach temperatures between fluids at economical pricing.
HeatX carries plate and frame exchangers to satisfy the high demands of DI water heat transfer. These are constructed of 304 or 316 stainless steel, Titanium, Hastelloy, Nickel, Incoloy, or Avesta SMO 254. Plate separation is handled by gaskets of various materials depending on your design requirements. Some of the choices in gasket materials include Nitrile (NBR), Silicone, EPDM, Viton, or Butyl.
The following is a list of typical processes that require a DI water heat exchanger: API or formulated pharmaceuticals, blood, plasma or growth media, WFI, USP, DI, RO and CIP heating /cooling, pure steam generation & condensing, bio kill & waste neutralization, and point of use cooling and/or heating.


